Smart city technologies have a high, and largely unrealized, potential to improve quality of life. The idea behind smart cities is to use technology and data purposefully to make better decisions and deliver a better quality of life. Beyond benefits in terms of safety, time, health, connectedness, jobs, and cost of living, huge improvements can be realized in the environmental sector. Smart-city solutions such as air quality monitoring, energy use optimization, and electricity, water, and waste tracking can produce results such as 10-15% fewer GHG emissions, 30-130 fewer kilograms of solid waste per person per year, and 25-80 liters of water saved per person per day.
Enlarge
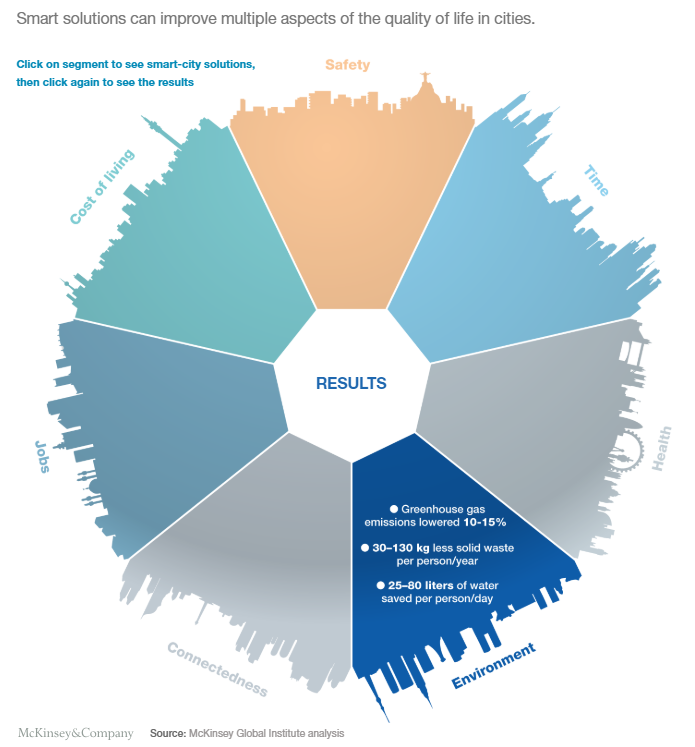
To achieve such benefits, three layers of smartness are required in a city, building on traditional physical and social infrastructure. First, the technology base includes networks of connected devices and sensors, such as smart phones connected by high-speed communication networks. Next, smart applications and data analysis capabilities are used to translate raw data into alerts, insights, and actions. Finally, wide adoption of applications and usage by cities, companies, and the public, together with the effective management of data, inspire better decisions and behavior change.
Smart applications contributing most to environmental improvements include (but are not limited to) those focused on mobility, water, energy, and waste. For example, real time public transit information and building automation systems can lead to fewer GHG emissions, better air quality can be realized as a secondary benefit of many energy saving and mobility applications, leakage detection and control can support water conservation, and digital tracking and payment for waste disposal can lead to solid waste reduction.
In a new study on smart cities, McKinsey Global Institute investigates how technology can deliver a better quality of life, including an analysis of smart applications that will be relevant for cities through 2025. Findings indicate that smart technologies could improve key indicators by 10–30% once introduced, and that using the current generation of smart city applications could effectively help cities make significant or moderate progress toward meeting 70% of the Sustainable Development Goals.
Read the full McKinsey Global Institute report: Smart Cities: Digital Solutions for a More Livable Future






