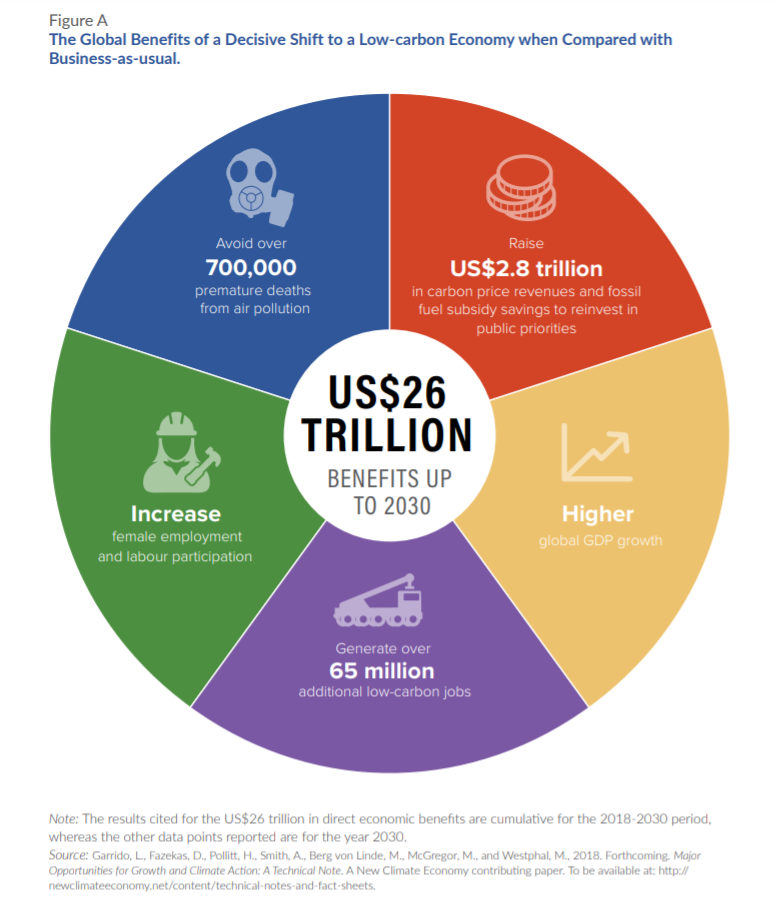
Strategic policy and investment decisions supporting the transition to a pathway of low-carbon, sustainable growth could lead to direct economic gains of US$26 trillion by 2030 compared to business-as-usual, according to a new report published by the Global Commission on the Economy and Climate through its New Climate Economy project.
Many of the decisions ultimately shaping the next 10 to 15 years will be made in the next 2 to 3 years, so we must act now to seize not only the economic, but also the social and environmental benefits of low-carbon and resilient growth. Focusing on the structural transformation in 5 key economic systems: energy, cities, food and land use, water, and industry, will provide the greatest potential for growth and the greatest possibility to reduce the risks of climate change. Priorities for urgent action are:
- Accelerating investment in sustainable infrastructure, supported by clear national and sub-national strategies and programs.
- Harnessing the power of the private sector, including to unleash innovation and advance supply chain transparency.
- Ensuring a people-centered approach, such that the gains are shared equitably and the transition is just.
Clean energy systems, smarter urban development, sustainable land use, wise water management, and a circular industrial economy are essential pieces to the puzzle. By 2030, ambitious action across these systems could generate over 65 million new low-carbon jobs, avoid over 700,000 premature deaths from air pollution, raise US$2.8 trillion in carbon price revenues and fossil fuel subsidy savings to reinvest in public priorities, increase female employment and labor participation, and lead to higher global GDP growth.
To achieve the benefits of this new growth approach and shift the world economy on to a more stable climate pathway, economic decisionmakers in both public and private sectors must take several steps:
- First, governments should put a price on carbon and move toward mandatory climate risk disclosure for major investors and companies.
- Second, all economies should place much greater emphasis on investing in sustainable infrastructure as a central driver of the new growth approach.
- Third, the full power of the private sector and innovation needs to be harnessed.
- Fourth, a people-centered approach is needed to ensure lasting, equitable growth and a just transition.
Recognizing that significant technological and market progress driving the shift to a new climate economy has been achieved over the last decade, The 2018 Report of the Global Commission on the Economy and Climate aims to motivate further action by economic and financial leaders in government and the private sector by highlighting the benefits of transitioning to a new growth path, identifying potential challenges, and defining actions to reap the benefits of stronger, cleaner, and more equitable growth.