Levels of the atmospheric greenhouse gases (GHGs) carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) have all reached new highs in 2017, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). This finding is based on data reported in the November 2018 issue of the WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin, which also suggests that there is no sign of a reversal in this trend.
“The last time the Earth experienced a comparable concentration of CO2 was 3-5 million years ago, when the temperature was 2-3°C warmer and sea level was 10-20 meters higher than now,” said WMO Secretary-General Petteri Taalas, when speaking of the record atmospheric levels of GHGs highlighted in the November Bulletin.
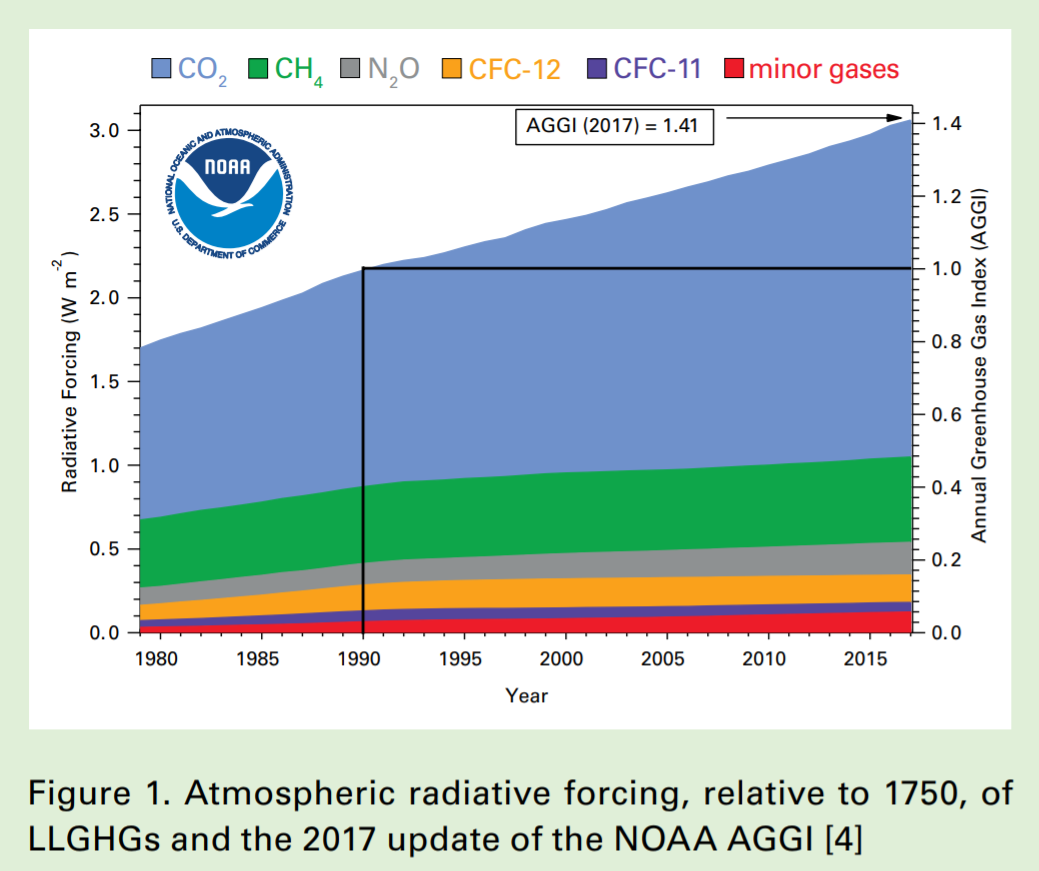
The Bulletin reports that globally averaged concentrations of CO2 reached 405.5 parts per million (ppm) in 2017, up from 403.3 ppm in 2016 and 400.1 ppm in 2015. Concentrations of methane and nitrous oxide also increased, while there was a resurgence of a potent greenhouse gas and ozone depleting substance called CFC-11, which is officially regulated under an international agreement to protect the ozone layer. These four GHGs, together with CFC-12, account for approximately 96% of radiative forcing – the warming effect on the climate – due to long-lived GHGs.
Enlarge
WMO GREENHOUSE GAS BULLETIN No. 14 | 22 November 2018
Since 1990, there has been a 41% increase in total radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases (see Figure 1). CO2, the most important anthropogenic GHG in the atmosphere, accounts for about 82% of the increase in radiative forcing over the past decade, according to figures from the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration quoted in the WMO Bulletin, and about 66% of total radiative forcing by long-lived GHGs. On the whole methane contributes approximately 17% of the radiative forcing by long-lived GHGs, while the third most important individual contributor, nitrous oxide, contributes approximately 6%.
In the lead up to the UNFCCC COP24 in Katowice next week, Mr. Taalas made the take away message from the fourteenth annual bulletin on greenhouse gas levels explicit, “The science is clear. Without rapid cuts in CO2 and other greenhouse gases, climate change will have increasingly destructive and irreversible impacts on life on Earth. The window of opportunity for action is almost closed.”
The Bulletin follows the release of the IPCC Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C (SR15), which shows that deep and rapid emission reductions will be needed in all sectors of society and the economy.






