2022 may be looked back on as a shed water moment in how we address the climate crisis. Not only because of the impacts of the Covid pandemic and the war in Ukraine, which has sent shockwaves through the global energy system, upending food security, and causing countries to re-evaluate their decarbonization strategies, but also because of the renewed emphasis coming from scientific research that shows that only through ambitious mitigation efforts and systemic transformation, can we avoid facing widespread limits to adaptation, and increased losses and damages.
A message that was, unfortunately, not seized upon during the COP27 in Egypt, which saw policymakers pitting mitigation and adaptation priorities against each other, and in the process turning back the hands of time to two decades ago when there was little understanding of the limits to adaptation and that adaptation without mitigation is both harder to achieve and exponentially more expensive.
Climate research conducted over the last year and presented in the report, 10 New Insights in Climate Science 2022 (10NICS), produced by Future Earth, The Earth League and World Climate Research Programme with the collaboration of the CMCC, gives a fresh set of new insights on the relationship between climate change and the global system.
By putting together 10 of the most important developments in climate change research, the report reveals the intricate web that links climate change and other risks, such as conflicts, pandemics, food crises and underlying development challenges.
This not only sheds light on the impacts of climate change and what is holding us back from addressing them but also puts forth a series of solutions that can help a wide range of stakeholders take effective action
What is new?
As temperatures continue to rise, it is becoming increasingly obvious that our ability to adapt to them decreases. This is the first insight of the Report which is also linked with the eighth one, whereby we can expect the impacts of loss and damage to continue to increase as we fail to adapt to spiraling climate change. Two issues that came to the forefront during the latest round of climate negotiations in Egypt, where the conflict between an adaptation and mitigation-focused approach took center stage.
Praised by many for its progress on Loss and Damage, the Cop27 was also largely criticized for its failure to address mitigation effectively. Yet scientific research highlights more than ever that ambition in both mitigation and adaptation needs to go hand in hand if dangerous tipping points are to be averted.
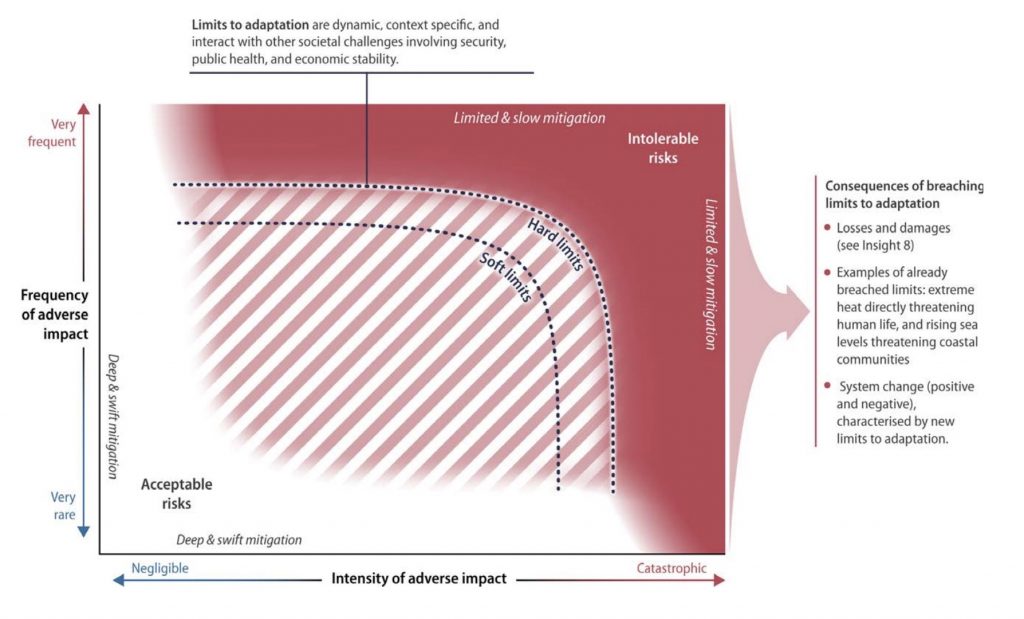
Researchers increasingly point out that we are already breaching adaptation limits, and adaptation will only become more difficult as we approach 1.5°C or even 2°C average global warming. Furthermore, vulnerability will tend to focus in “hotspots” (insight 2) where climate, economic and social sensitivity is highest. In these areas, the ability for adaptation is lowest, and the “triple planetary crisis” of biodiversity loss, pollution and climate change cause an even greater stress on local food, water, energy and human health and safety (insight 5).
In fact, just as in the 2021 Report, the impacts of climate change on human physical and mental health are becoming increasingly well documented (insight 3) and how this will continue to lead to involuntary migration and displacement (insight 4).
Progress towards solutions
Yet the report also chooses to focus on solutions, one of the most important of which will be integrated land management and how this can bring benefits both for people and ecosystems (insight 6). Yet new studies continue to highlight that as long as global temperatures continue to rise, our ability to predict how natural carbon sinks will behave is upended, leading to researchers recommending that GHG emissions from land based activities should be kept to a minimum and natural ecosystems should be preserved and maintained as much as possible.
For this to be achieved, research shows now more than ever that solutions have to be implemented using inclusive decision-making as this has the to power to create more effective climate-resilient development (insight 9).
One of the main solutions to the climate crisis has long been thought to be private finance. Yet the latest research shows that this is failing to implement the transformative change that many had hoped for (insight 7). From greenwashing to lack of established metrics, there is much room for improvement, although the potential impact of large institutional investors is also seen as an area of positive change in the near future.
Finally, one of the true keys to pervasive change is shown to be overcoming the structural obstacles that have led to a marriage of policy, industry and societal goals that are fuel for resource extraction and therefore increased emissions. Addressing this interconnected web of interests is seen by researchers as a key priority for effective policymaking that addresses the climate crisis.
“The latest science confirms the rising social costs of severe climate extremes and the urgent need to deviate away from risks of going beyond limits to adaptation and crossing irreversible tipping points. As science advances, we have more evidence of massive costs, and risks but also global benefits of reduced loss and damage through an orderly, safe landing of the world within the Paris climate range. To succeed requires global collaboration and speed at an unprecedented scale,” says Professor Johan Rockström, co-chair of the Earth League, the Earth Commission and Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in the Report’s Press Release.
Cover picture: Maize intercropped with red amaranth | Red amaranth (a leaf vegetable widely used in Bangladesh) helps to control weeds and conserve soil moisture. Photograph: D.B. Pandit/CIMMYT (CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)