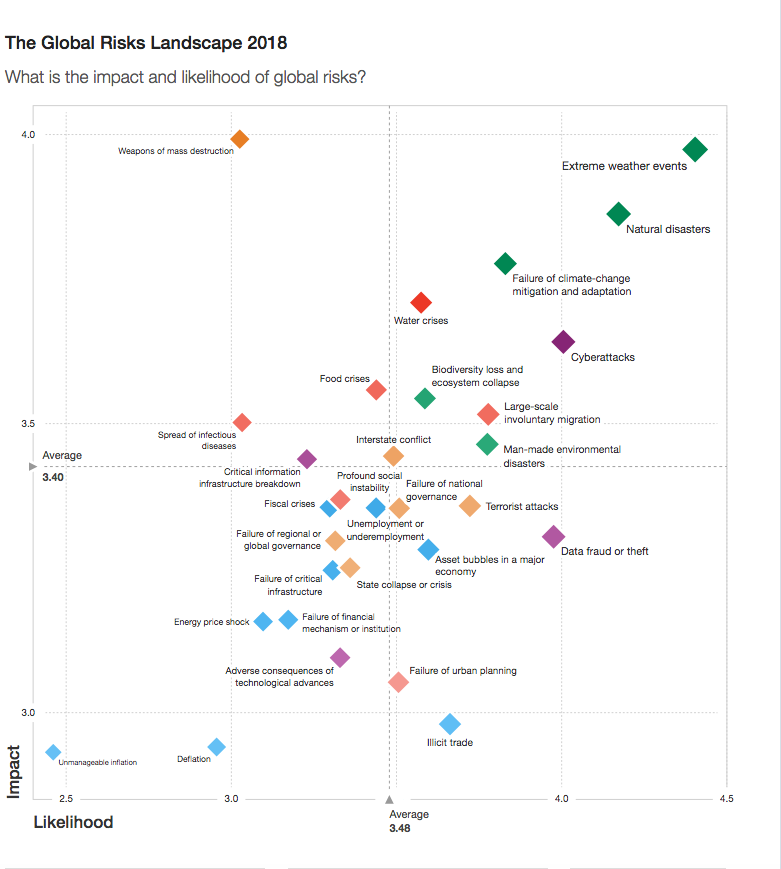
Environmental threats dominates the landscape depicted by the Global Risks Report 2018, the latest report released by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
The 2018 edition of the annual WEF flagship publication lists extreme weather events, natural disasters and failure to implement sufficient climate change mitigation and adaptation among the five threats most likely to occur in the next 10 years. The WEF also points to the rise in CO2 emissions in 2017 (the first time in the past four years) as a sign of the growing urgency for concerted climate action.
Based on consultation with nearly 1,000 experts and decision-makers, the report places all five environmental risks – extreme weather events, biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse, major natural disasters, man-made environmental disasters and failure of climate-change mitigation and adaptation – among the above-average concerns in terms of likelihood and impact.
Extreme weather events emerge as the single most prominent risk (see the graph below – click to enlarge – and explore all results of the Global Risks Report 2018).
Above all, the study warns against the deep interconnections both among environmental risks and between them and risks in other categories, such as water and food crises and involuntary migration.
The 2018 edition introduces a new focus exploring 10 potential “Future Shocks” that may affect a world increasingly more complex and interconnected, in which sudden and dramatic breakdowns, such as dramatic disruptions of food supply, out-of-hand AI proliferation, democratic collapses and spiralling cyber conflicts, become more likely.
As global economic growth is picking up, the improved economic outlook gives room for leaders to tackle systemic and increasing fragility affecting societies, economies, international relations and the environment, the report says.