Source: World Economic Forum press release
Is the world sleepwalking into a crisis? Global risks are intensifying but the collective will to tackle them appears to be lacking. Instead, divisions are hardening. The world’s move into a new phase of strongly state-centred politics, noted in the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report 2019, continued throughout 2018.
The report, which incorporates the results of the annual Global Risks Perception Survey of approximately 1,000 experts and decision-makers, points to a deterioration in economic and geopolitical conditions. Trade disputes worsened rapidly in 2018 and the report warns that growth in 2019 will be held back by continuing geo-economic tensions, with 88% of respondents expecting further erosion of multilateral trading rules and agreements.
“With global trade and economic growth at risk in 2019, there is a more urgent need than ever to renew the architecture of international cooperation. We simply do not have the gunpowder to deal with the kind of slowdown that current dynamics might lead us towards. What we need now is coordinated, concerted action to sustain growth and to tackle the grave threats facing our world today,” said Børge Brende, President of the World Economic Forum.
Environmental threats continue to dominate the landscape depicted by the report for the third year in a row.
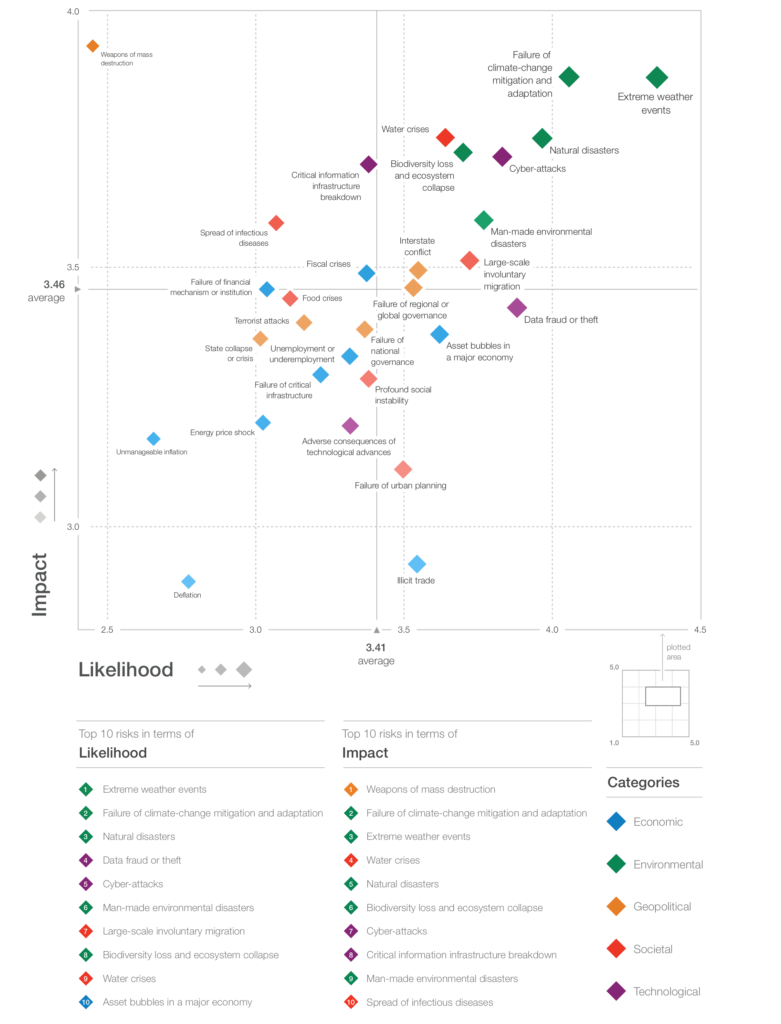
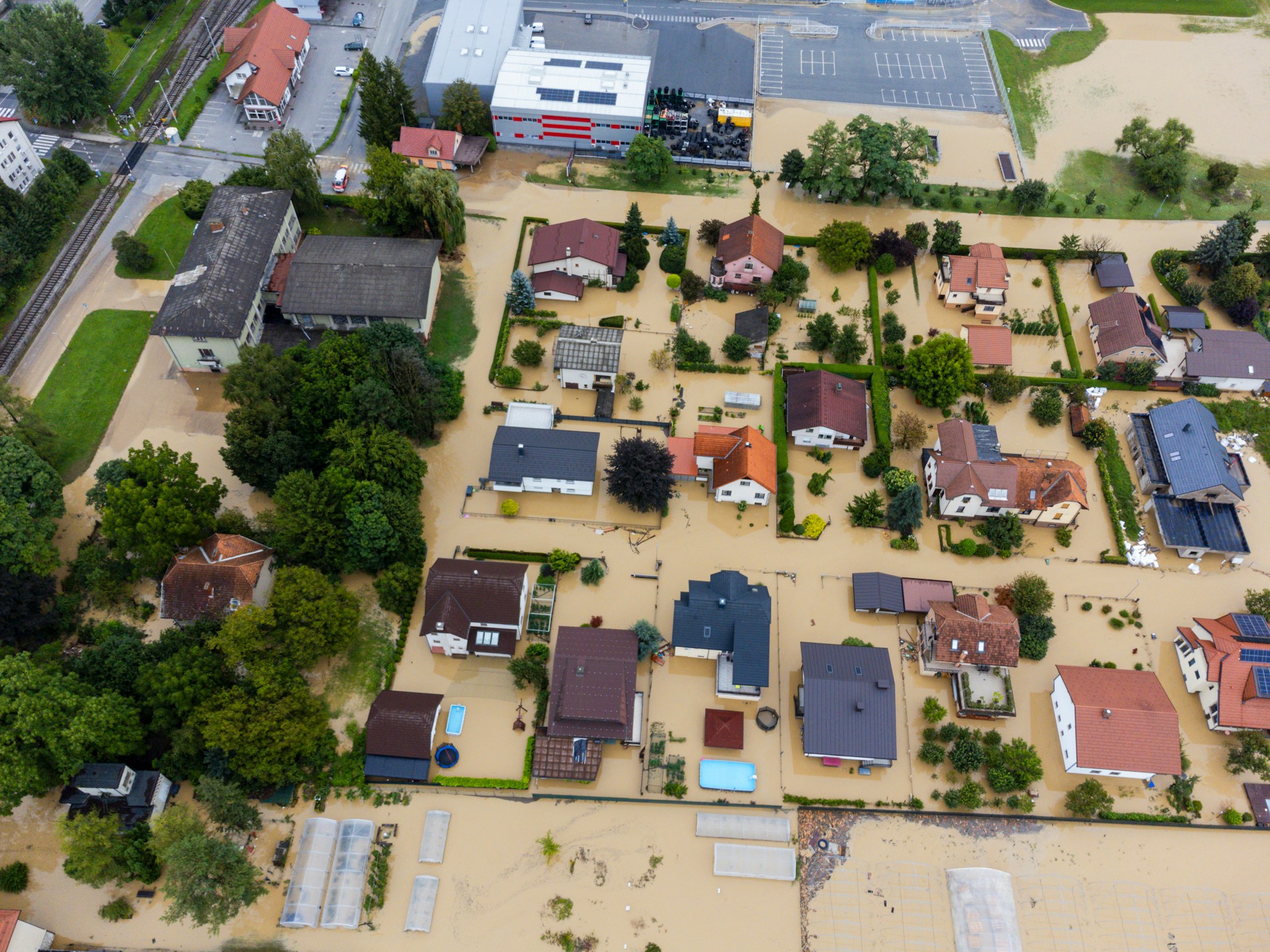
The 2019 edition of the annual WEF flagship publication lists in fact extreme weather events, failure to implement sufficient climate change mitigation and adaptation and natural disasters among the top five threats most likely to occur in the next 10 years.
More in detail, extreme weather events appear as the risk of greatest concern, but the survey respondents are increasingly worried about environmental policy failure: having fallen in the rankings after Paris, “failure of climate-change mitigation and adaptation” jumped back to number two in terms of impact this year. Moreover, the results of climate inaction are becoming increasingly clear. The accelerating pace of biodiversity loss is a particular concern. As reported in the Living Planet Index, which tracks more than 4,000 species across the globe, species abundance is down by 60% since 1970. In the human food chain, biodiversity loss is affecting health and socioeconomic development, with implications for well-being, productivity, and even regional security.
Environmental risks also pose problems for urban infrastructure and its development. With sea levels rising, many cities face hugely expensive solutions to problems that range from clean groundwater extraction to superstorm barriers. Shortfalls of investment in critical infrastructure such as transport can lead to system-wide breakdowns as well as exacerbate associated social, environmental and health-related risks.
The report provides first a picture of the global risks landscape and warns of the danger of sleepwalking into crises. Then, It goes on to consider a number of risks in depth: geopolitical and geo-economic disruptions, rising sea levels, emerging biological threats, and the increasing emotional and psychological strain that many people are experiencing. The Future Shocks section again focuses on potential rapid and dramatic changes in the systems we rely on – topics this year include weather manipulation to stoke geopolitical tensions, such as cloud seeding to induce or suppress rain, quantum computing, human rights and economic populism. These “what if” scenarios are food for thought as world leaders assess potential shocks that might rapidly and radically disrupt the world.
“The world is facing a growing number of complex and interconnected challenges—from slowing global growth and persistent economic inequality to climate change, geopolitical tensions and the accelerating pace of the Fourth Industrial Revolution”, the report says, while highlighting the need for a collaborative and multi-stakeholder approach to address global problems.
For more information on the Global Risks Report 2019:
- Read the full report
- Watch the report launch press conference here
- Read the Forum Agenda here