Source: World Health Organization Press Release
A recent report by WHO highlights why health considerations are critical to the advancement of climate action, and outlines key recommendations for policymakers. The report was launched at COP24 in Katowice, Poland, where world leaders gathered from 2 to 14 December to finalize the rulebook of the implementation guidelines of the 2015 Paris Agreement and discuss ways to step up ambition.
Exposure to air pollution causes 7 million deaths worldwide every year and costs an estimated US$ 5.11 trillion in welfare losses globally. In the 15 countries that emit the most greenhouse gas emissions, the health impacts of air pollution are estimated to cost more than 4% of their GDP. Actions to meet the Paris goals would cost around 1% of global GDP.
“The Paris Agreement is potentially the strongest health agreement of this century,” said Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director-General of WHO. “The evidence is clear that climate change is already having a serious impact on human lives and health. It threatens the basic elements we all need for good health – clean air, safe drinking water, nutritious food supply and safe shelter – and will undermine decades of progress in global health. We can’t afford to delay action any further.”
The same human activities that are destabilizing the Earth’s climate also contribute directly to poor health. The main driver of climate change is fossil fuel combustion which is also a major contributor to air pollution.
Enlarge
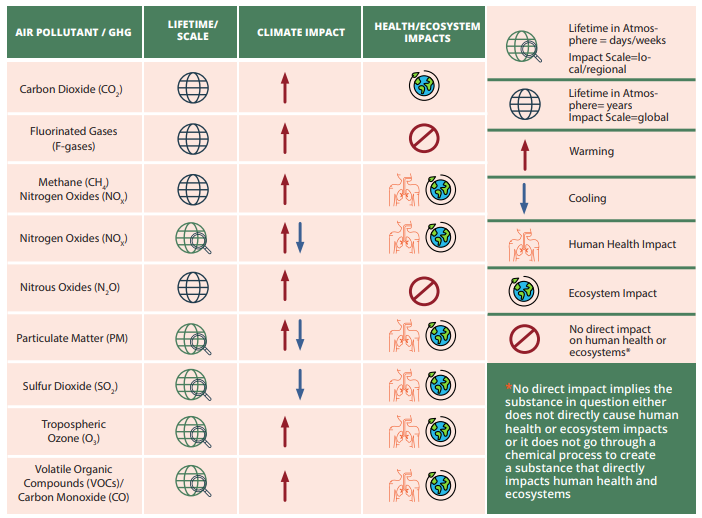
climate and health. Source: COP24 special report: health and climate change, World Health Organization 2018
“The true cost of climate change is felt in our hospitals and in our lungs. The health burden of polluting energy sources is now so high, that moving to cleaner and more sustainable choices for energy supply, transport and food systems effectively pays for itself,” says Maria Neira, WHO Director of Public Health, Environmental and Social Determinants of Health. “When health is taken into account, climate change mitigation is an opportunity, not a cost.”
Switching to low-carbon energy sources will not only improve air quality but provide additional opportunities for immediate health benefits. For example, introducing active transport options such as cycling will help increase physical activity that can help prevent diseases like diabetes, cancer and heart disease.
WHO’s COP-24 Special Report: health and climate change provides recommendations for governments on how to maximize the health benefits of tackling climate change and avoid the worst health impacts of this global challenge.
It describes how countries around the world are now taking action to protect lives from the impacts of climate change – but that the scale of support remains woefully inadequate, particularly for the small island developing states, and least developed countries. Only approximately 0.5% of multilateral climate funds dispersed for climate change adaptation have been allocated to health projects.
Pacific Island countries contribute 0.03% of greenhouse gas emissions, but they are among the most profoundly affected by its impacts. For the Pacific Island countries, urgent action to address climate change — including the outcome of COP24 this week — is crucial to the health of their people and their very existence.
“We now have a clear understanding of what needs to be done to protect health from climate change – from more resilient and sustainable healthcare facilities, to improved warning systems for extreme weather and infectious disease outbreaks. But the lack of investment is leaving the most vulnerable behind,” said Joy St John, Assistant Director-General for Climate and Other Determinants of Health.
Read more:






