Addressing the nexus between biodiversity and climate change is about discussions on nature and nature based solutions. From ecosystem-based approaches to green infrastructure and urban greening, biodiversity holds the key to solving a wide range of climate-related issues. However, understanding the meaning behind umbrella terms such as nature based solutions is only the first step.
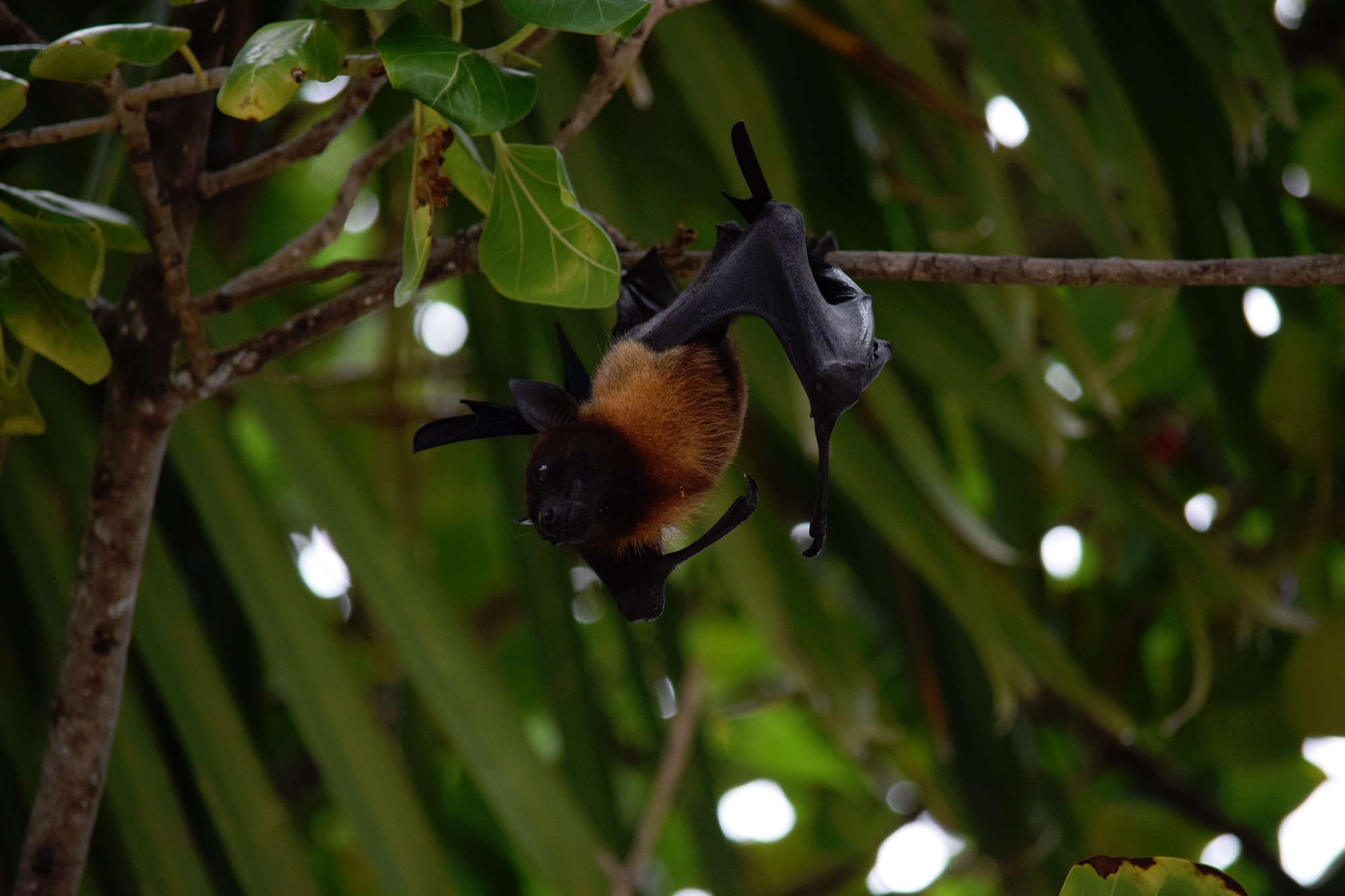
With one in four species currently under threat of extinction, part of the solution involves understanding which species are better equipped to adapt, and hence survive, so as to improve conservation efforts and policy choices.
Biodiversity has an intrinsic value in and of itself and part of that is tapping into the potential of natural capital, which at its core involves challenging our understanding of the relationship between economy, society, and the environment.
Yet biodiversity is not just about jungles and pristine nature. It’s also about how we integrate nature into our cities and how we include biodiversity concerns into our agricultural industry, with concepts such as agrobiodiversity. Cities and societies of the future will require this.
Programs that advance understanding of the links between species and community traits, ecological functions and ecosystem services – both on land and at sea – and how they are impacted by climate change are crucial and will require precise data and effective ecosystem management and monitoring.
Biodiversity is part of the solution.